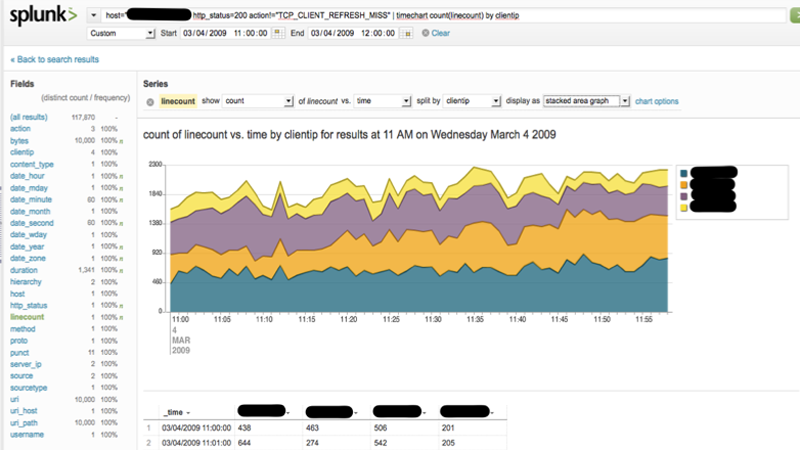
I recently hooked up Splunk with AWS to search, monitor, and analyze log files. Splunk indexes data on read and allows for super-fast searching and visualization. I like to think of Splunk as Google Search for log files with visualization built-in.
Benefits
- Allow for real time log analysis
- Allow for faster historical log analysis
- Provide data access to non-technical users who don’t know Hadoop
- Provide access to previously untapped data
- Promote transparency
Competitors
Here's a good article comparing Splunk vs ELK and a Quora post detailing free alternatives to Splunk.
Product Overview: Splunk Free, Enterprise, Storm, Cloud
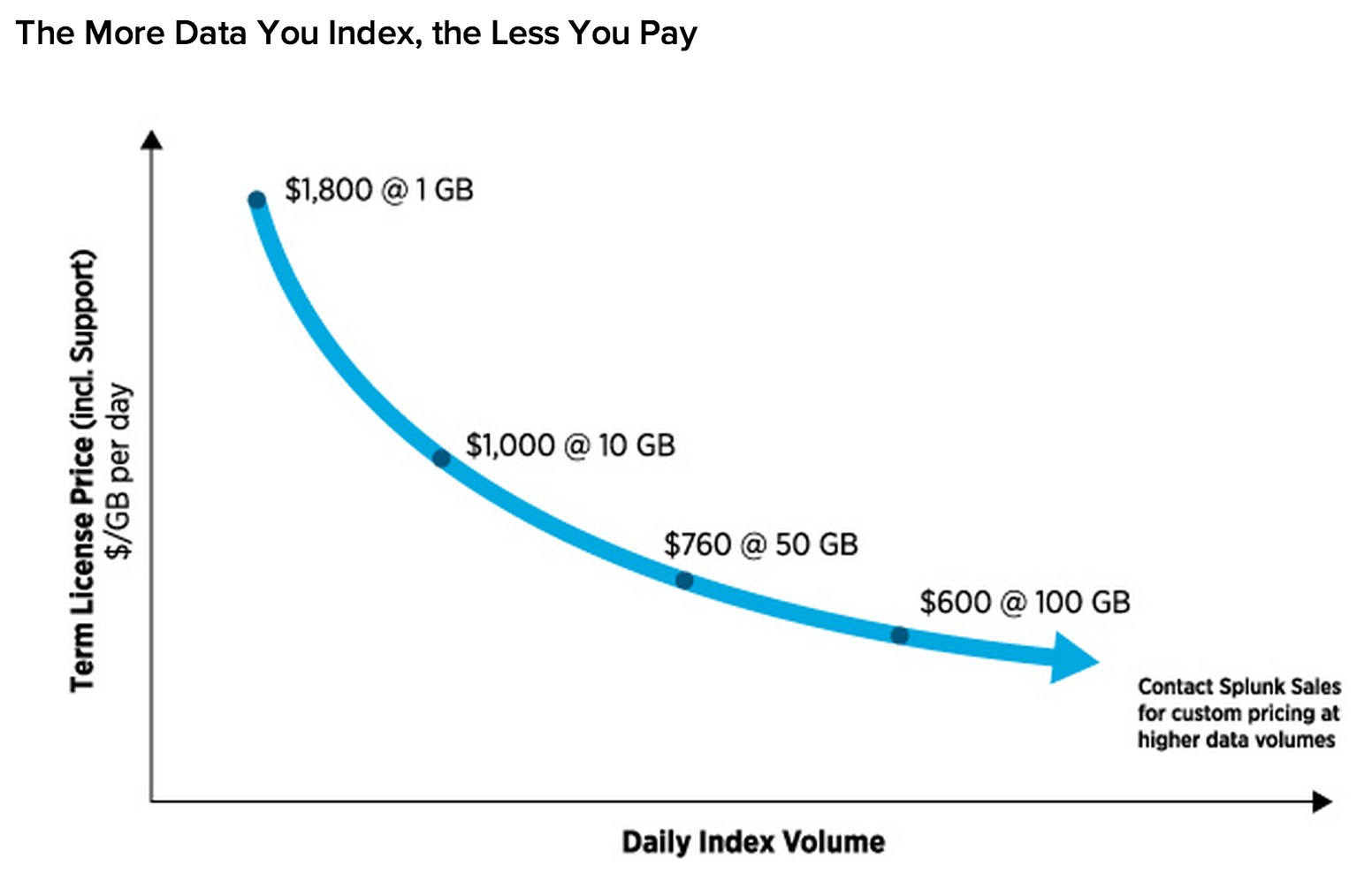
Splunk has an interesting licensing model where the cost per GB of daily indexing decreases the more you index. For example, indexing 1 GB per day would cost $1800 (1 GB x $1800), whereas indexing 10 GB per day would cost $10000 (10 GB x $1000).
Splunk Enterprise is a "bring your own license" model and requires you to host the server(s).
Splunk Free is similar to Splunk Enterprise and allows you to index 500 MB per day.
Splunk Storm is a free version of Splunk Cloud that allows for 20 GB of storage and 30 days of data retention. You can have five project members and three projects. It was recently announced that Splunk Storm will no longer be supported.
Splunk Cloud is a hosted solution of Splunk Enterprise without the restrictions of Splunk Storm. Splunk Cloud includes 5 GB daily indexing, 90 days of storage, and a 100% uptime SLA.
Cost Comparison: Splunk Enterprise vs Splunk Cloud
If hosting Splunk Enterprise on AWS, you must factor in the cost of compute, storage, bandwidth, server administration, etc. For example:
- c3.xlarge for one year on-demand costs $1840*
- 1 TB general purpose SSD costs $1164
*4 EC2 Compute Units and 7 GB of RAM is recommended for daily indexing of < 20 GB according to Splunk Answers
Just factoring in the Splunk Enterprise license, compute costs, and EBS costs (no bandwidth, server administration, etc) totals $4804. Splunk Enterprise seems like a fair choice if just starting out with Splunk with low daily index volumes. Splunk Cloud becomes more appealing for larger workloads (up to 5 GB daily included) or for those who wish to have more of a turnkey solution. Splunk Cloud also runs a c3.4xlarge which has 16 EC2 Compute Units and 30 GB of RAM.
Splunk slashed prices for its cloud offering by 33% in August of 2014 in response to price cuts from Amazon. Amazon has dropped prices over 40 times over the last six years.
Getting Started: Splunk on the AWS Market Place
The easiest way to get started with Splunk Enterprise on AWS is to spin up a Splunk instance from the AWS Market Place. There are no additional charges per hour other than what you would pay Amazon for compute.

Setup a Splunk IAM Account
Create an IAM account that Splunk will use to access your AWS. Enter the IAM credentials in the Splunk for AWS plugin. The following sections describe what IAM permissions are required for each AWS feature.
Setup Splunk for S3
Create the S3 bucket and related objects.
Add IAM List and Get permissions for buckets and for objects in buckets.
Setup Splunk for CloudTrail
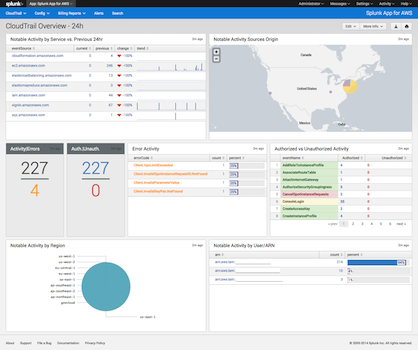
Setup Simple Queue Service (SQS) to subscribes to the Simple Notification Service (SNS) notification events from CloudTrail:
- Enable CloudTrail
- Create an S3 Bucket for CloudTrail events
- Enable SNS Notifications
- Create an SQS
- Subscribe to the SNS Notifications that you enabled
Add IAM permissions for the following:
| AWS Product | IAM Permission |
|---|---|
| CloudTrail | CloudTrail Read Only Access |
| S3 bucket that collects your CloudTrail logs | Get (and Delete only if you want to delete bucket log files after loading them into Splunk) |
| SQS subscribed to the S3 bucket that collects CloudTrail logs | ReceiveMessage, SendMessage, ListQueues, GetQueueUri |
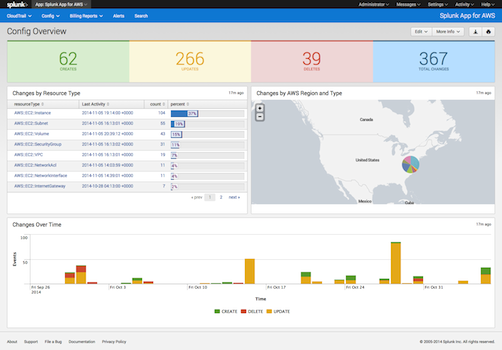
Setup Splunk for Config
Config setup is similar to CloudTrail. Refer to the instructions for CloudTrail, substituting Config for CloudTrail.
Setup Splunk for CloudWatch
CloudWatch requires no additional configuration for Splunk other than Describe, List, and Get IAM permissions.
Setup Splunk for Billing
Review the AWS documentation to turn on AWS billing reports.
Add IAM billing permissions for ViewBilling and ViewUsage.
Setup Splunk Indices
Create one index per data input. For example, the index aws-billing would correspond to to the AWS billing feature. Be careful with naming indices, as Splunk requires the following indices to be named the following:
- CloudTrail: aws-cloudtrail
- Config: aws-config
If you decide to change the names of the indices for CloudTrail and Config, you'll have to update the macros.conf config files.
Setup Splunk Data Inputs
Create one data input and match it up with an index. Note Splunk requires the following data input sources for Cloudtrail and Config to be named the following:
- aws:cloudtrail
- aws:config
Search and Visualize!
You should now be able to search and visualize AWS.